
March 10, 2022 | 6 minute read
6 Market trends causing the global shift from MPLS to the Internet
Omdia
Brian Washburn, Research Director, Service Provider Enterprise & Wholesale
Enterprise MPLS VPN services had a tremendous run. More than 20 years after its debut this private IP technology is still important. But MPLS VPN services have crested and now entered revenue decline in favor of global internet alternatives.
Enterprises are converting portions of their MPLS VPNs to public Internet access: dedicated and broadband Internet access is replacing MPLS VPN ports. Business spend on broadband and dedicated Internet services is increasing.
Meanwhile, Omdia expects nearly 40% of enterprise MPLS revenue to be reallocated to other budget priorities over the next five years. Below we list the six market trends that are leading enterprise MPLS into decline.
6 trends making enterprises move away from MPLS
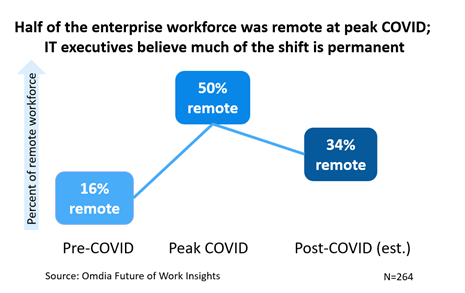
#1 The move from the office to remote working
Among large multinational corporations (i.e., present in five or more countries), COVID caused remote workers to skyrocket from 16% of the workforce to roughly half of workers.
Remote workers have forced enterprise IT to adopt user applications that work with home broadband as the lowest common denominator. As COVID eventually tapers, fewer offices and on-site workers will remain. This affects the number and size of MPLS ports to work offices.
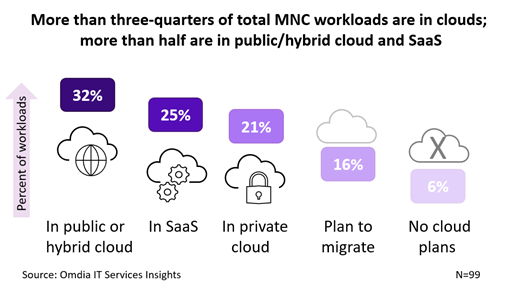
#2 From data center to cloud workloads
The average multinational corporation has already ported about one-third of its applications’ workloads to public/hybrid cloud, led by major enterprise software such as:
- Resource planning
- Supply chain/logistics
- Customer management
Another 25% of applications workloads have shifted to SaaS, led by unified communications and accounting/human resources. Less than one-quarter of conventional applications are not yet cloud-enabled, and roadmaps are in place to shift over most remaining workloads. Many cloud-enabled applications, particularly SaaS, deliver an acceptable user experience over the public Internet without the consistent performance of MPLS.
#3 A shift from routers to SD-WAN
SD-WAN cannot overcome poor-quality networks. But SD-WAN separation of applications overlay from network underlay can let enterprises mix connections to test and swap out among networking options.
The legacy design of a pair of identical MPLS circuits from two diverse providers to every location is still the gold standard. With SD-WAN, an enterprise may swap out MPLS ports for Internet services at locations of its choice, and at its own pace.
Network administrators can approach port swaps as carefully or aggressively as the business demands.
#4 Demand for performance-optimized Internet over best-effort
The traditional solution to best-effort network performance issues is to throw bandwidth at the problem. This does not always work. Some service providers, using network design and optimization techniques, offer global premium business Internet with basic traffic guarantees for latency and packet delivery. These guarantees can be enough for an enterprise to no longer need a global MPLS backbone for most applications traffic.
#5 Changing priorities from security concerns to preferred models
An MPLS separate from public networks was considered a safe option for maintaining integrity around a network perimeter. But organizations operate their Internet access side-by-side with private WAN.
Enterprises also have in-person and remotely connected workforces, a sea of personal and corporate computer devices, and critical third-party interconnection points. This perimeter-less network needed a new type of security model spanning all communications and devices. A new zero-trust model puts the focus on applications and devices and makes the private MPLS network perimeter less relevant.
#6 Flexibility and cost per bit
Finally, Internet services are universally available and fast to provision. With a few exceptions, the cost and provisioning interval to extend Internet access to a new location is substantially less than for MPLS. Enterprises can choose among ISPs and preferred methods of access. They can work through a partner to manage ISPs.
One by one, enterprises’ reasons to keep MPLS VPN services everywhere are evaporating. Public Internet alternatives are more flexible, less costly per bit, can be adequately optimized, secured, and can be swapped in for MPLS at enterprises’ discretion. The work-office and data-center model that reinforced the private WAN has given way to remote work and cloud-hosted applications. MPLS VPN does not go away, but enterprises will limit use to where it is needed.
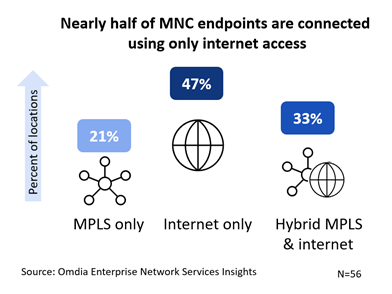
How many enterprises are making the switch from MPLS to the Internet?
The conversion of sites from MPLS-only, to hybrid MPLS/Internet, to all-Internet is happening rapidly. In early 2020, MNCs estimated that:
- 60% of their sites were connected via MPLS/dual-MPLS only
- 15% were hybrid MPLS/internet VPN,
- 25% were connected by internet only
About two years later, enterprises have flipped. Internet-only sites are the largest segment, and MPLS/dual-MPLS only locations have shrunk to 21% of sites.
This aligns with Omdia’s one-on-one interviews of enterprise executives’ perspectives. A few years ago, organizations historically tied to MPLS had started exploring migrating select ports to the Internet. At the time, they generally clustered around an 80/20 rule (maintain 80% of the MPLS network, migrate 20% to public Internet). Today, the situation has flipped with enterprise executives. Plans now call for operating 80% of the corporate network on public Internet, keeping just 20% of MPLS ports to the company’s data centers, major locations, and key interconnect points.
The Internet options have also become more varied and widely available: dedicated and broadband fiber-based services, and 4G/emerging 5G are among the range of Internet access options that executives are exploring.
Based on Omdia’s executive interviews, Internet migration is not always easy or pain-free. Large enterprise MNCs tap partners to help in the move from MPLS to Global Internet, and in the shift from conventional routers to SD-WAN.
Partner-managed network services providers can help to choose the best-suited platform for your requirements, assess the proper configuration for your network underlay and applications overlay, and provide ongoing support with a Global Internet fabric that has both many ISPs and many devices under management.
*Where Omdia references multinational corporations (MNCs) in its survey research, results represent organizations doing business in five or more countries.
Looking for a Managed Service Provider who can help you with the switch from MPLS to the Internet?
With Managed SD-WAN from Expereo, you get the fast, reliable application performance that you need to deliver differentiated IT experiences.
Get in touch today to discuss your needs.
Share to
Omdia
Brian Washburn, Research Director, Service Provider Enterprise & Wholesale
Omdia is a leading research and advisory group focused on the technology industry. With clients operating in over 120 countries, Omdia provides market-critical data, analysis, advice and custom consulting.
More articles from OmdiaStay connected with Expereo
Be the first to hear about our latest insights, news, and updates.
